ISTC NEWS

Early American ‘Medicine’ Probed by Archaeometry
Life was hard in 1850. Tuberculosis (consumption) was rampant, and one was likely to be dead by 40. The tubercle bacillus was not discovered until 1882, and was not treatable until the early 1940s. By 1900 more than 80 percent of the U.S. population was infected before age 20.
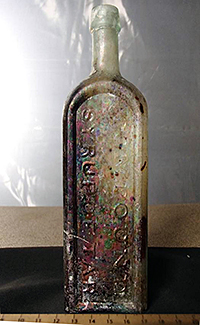
A ‘medicine’ bottle discovered by Illinois State Archaeological Survey (ISAS) during a dig at Meredosia, Illinois, gives evidence of the desperation they faced. Both ISTC and ISAS are divisions of the Prairie Research Institute.
The contents were analyzed by John Scott, senior analytical chemist at ISTC, revealing a dangerous stew of heavy metals and polyaromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs). Scott presented his findings Feb. 19 during ISAS’s Fourth Ancient Technologies and Archaeological Materials Symposium at the University of Illinois.
The bottle, labeled “Thomson’s Compound/Syrup of Tar/For Consumption,” came from a the excavation of a house cellar yielding artifacts from the 1840s and 1850s.
News articles and advertisements of the time are replete with testimonials of ‘health’ and ‘vigor’ from drinking the compound. Many patent medicines contained a lot of alcohol, which would have been needed to keep the other ingredients in suspension, Scott suggested.
The analysis showed compounds consistent with coal tar, pine tar, and essential oils suggesting cumin and thyme. All 16 priority PAHs, now

regulated by the U.S. EPA as carcinogens, were present. For comparison, Thomson’s remedy measured a priority PAHs content in concentrations almost three-and-a-half times greater than the mean for crude oil.
Many ‘remedies’ of the era also soothed ‘symptoms’ of various maladies by including opium, morphine, heroin, cocaine, chloroform, methamphetamine, or barbiturates.
Scott found strong evidence that the Thomson’s was spiked not just with alcohol, but also with the active compound in marijuana. High resolution mass spectrometer measurements showed no sign of morphine, cocaine or the other drugs, but demonstrated clear peaks indicating THC (delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol) – which is found in marijuana.

Nine metals were detected in Thomson’s Compound. Arsenic, lead, and iron exceeded levels now considered acceptable for pharmaceuticals. Manganese was close to that limit.
“We can’t know how much of the Thomson mixture was left in the bottle when it was disposed of,” Scott said. “But even if it evaporated from a full bottle, this was a potent brew.”
The name Thomson was synonymous with medicine throughout much of the 19th century, ever since Samuel Thomson succeed in patenting his system of botanic medicine in 1813. Originally a reaction against orthodox medicine, Thomson sought to demystify healing arts for the average man with remedies of natural herbs and extracts. The lucrative field drew many competitors, knock-off artists, and experimenters. For example, a different ‘Samuel Thomson’ was responsible for the Meredosia artifact!

