by Lois Yoksoulian – Physical Sciences Editor of U of I News Bureau
Microplastics contaminate the world’s surface waters, yet scientists have only just begun to explore their presence in groundwater systems. A new study is the first to report microplastics in fractured limestone aquifers – a groundwater source that accounts for 25 percent of the global drinking water supply.
The study identified microplastic fibers, along with a variety of medicines and household contaminants, in two aquifer systems in Illinois. The findings are published in the journal Groundwater.
“Plastic in the environment breaks down into microscopic particles that can end up in the guts and gills of marine life, exposing the animals to chemicals in the plastic,” said John Scott, a researcher at the Illinois Sustainable Technology Center and study co-author. “As the plastics break down, they act like sponges that soak up contaminants and microbes and can ultimately work their way into our food supply.”

Groundwater flows through the cracks and voids in limestone, sometimes carrying sewage and runoff from roads, landfills and agricultural areas into the aquifers below, Scott said.
The researchers collected 17 groundwater samples from wells and springs – 11 from a highly fractured limestone aquifer near the St. Louis metropolitan area and six from an aquifer containing much smaller fractures in rural northwestern Illinois.
All but one of the 17 samples contained microplastic particles, with a maximum concentration of 15.2 particles per liter from a spring in the St. Louis area, the study reports. However, deciphering what that concentration means is a challenge, Scott said. There are no published risk assessment studies or regulations.
The researchers did find, however, that concentrations from their field areas are comparable to those of surface water concentrations found in the rivers and streams in the Chicago area, said Samuel V. Panno, an Illinois State Geological Survey researcher and lead author of the study.
“The research on this topic is at a very early stage, so I am not convinced we have a frame of reference to state expectations or bounds on what is considered low or high levels,” said Tim Hoellein, a biology professor at Loyola University Chicago and study co-author. “Our questions are still basic – how much is there and where is it coming from?”
The researchers identified a variety of household and personal health contaminants along with the microplastics, a hint that the fibers may have originated from household septic systems.
“Imagine how many thousands of polyester fibers find their way into a septic system from just doing a load of laundry,” Scott said. “Then consider the potential for those fluids to leak into the groundwater supply, especially in these types of aquifers where surface water interacts so readily with groundwater.”
There is still a monumental amount of work to be done on this subject, Scott said. He anticipates that microplastic contamination in both surface water and groundwater will be a problem for years to come.
“Even if we quit plastics cold turkey today, we will still deal with this issue for years because plastic never really goes away,” Scott said. “It is estimated that 6.3 billion metric tons of plastic waste have been produced since the 1940s, and 79 percent of that is now in landfills or the natural environment. To me, it is such a weird concept that these materials are intended for single use, yet they are designed to last forever.”
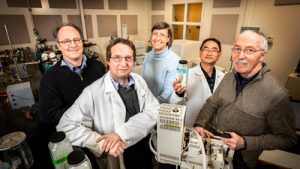
Walton R. Kelly of the Illinois State Water Survey; Wei Zhang and Nancy Holm of ISTC; Rachel E. McNeish of California State University, Bakersfield; Timothy J. Hoellein of Loyola University, Chicago; and Elizabeth L. Baranski of the League of Women Voters of Jo Daviess County also contributed to this research. The ISGS, ISWS and ISTC are part of the Prairie Research Institute at the University of Illinois at Urbana Champaign.
The League of Women Voters of Jo Daviess County, ISGS, ISWS, ISTC, Illinois-Indiana Sea Grant of the National Oceanic Atmospheric Administration and the National Science Foundation supported this research.


 Twenty-seven Illinois companies and organizations were honored on October 23 for their significant achievements in protecting the environment, helping sustain the future, and improving the economy. The winners were announced during a ceremony at the Union League Club in Chicago. Read winners summaries in
Twenty-seven Illinois companies and organizations were honored on October 23 for their significant achievements in protecting the environment, helping sustain the future, and improving the economy. The winners were announced during a ceremony at the Union League Club in Chicago. Read winners summaries in 




 The U of I system will be demonstrated over a two-month period at
The U of I system will be demonstrated over a two-month period at 

 The technology demonstration was one of ISTC’s Billion Gallon Water Challenge (BGWC) research projects which aimed at saving freshwater resources at multiple levels. A case study on this and other
The technology demonstration was one of ISTC’s Billion Gallon Water Challenge (BGWC) research projects which aimed at saving freshwater resources at multiple levels. A case study on this and other