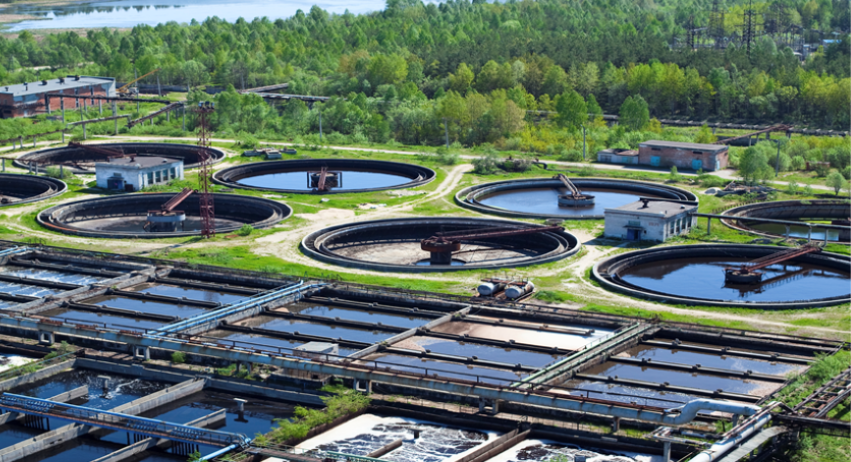
A considerable amount of energy is used to treat and deliver water on a daily basis. Due to the rising cost and impact of that process, ISTC has made a deep commitment to work with organizations in looking for ways to conserve resources and cut costs.
The Technical Assistance Program (TAP) at the Illinois Sustainable Technology Center (ISTC) makes companies and communities more competitive and resilient with sustainable business practices, technologies, and solutions. TAP works at the intersection of industry, science and government to help clients achieve profitable, sustainable results. As a change agency, ISTC partners with clients to improve use of water by improving efficiencies in distribution systems, water consumption and wastewater generation.
TAP focused assessment provides a detailed picture of a site’s water use and consumption patterns. Engineers identify industry best practices, provide cost analysis, payback and environmental benefits. TAP has worked with clients across industry sectors to expose solutions to unnecessary water consumption and wastewater generation, often eliminating costly, recurring wastewater treatment facility surcharges or hazardous waste disposal charges.
ISTC’s technical assistance strategic focus areas for its WatcH20 Program include:
Water use assessments and audits
Commercial and Industrial building audits include a water use assessment and fixture inventory to provide an evaluation that identifies efficiency priorities based on the shortest payback periods. Water usage habits and behaviors are also analyzed with recommendations provided to maximize conservation efforts.
Process specific analysis
ISTC conducts comprehensive analysis of process water including process mapping, metering, data collection, and calculating the full cost of water in the process. Alternative methods can be investigated along with economic analysis of potential changes.
Water purification, reclamation and reduction
ISTC research engineers are skilled at developing and applying the latest technologies to purify and reclaim water and water-based chemistry in a wide variety of industrial and sanitary applications. In addition, ISTC engineers have significant experience with the implementation of conservation technologies (conductivity controls, counter current rinsing, flow restrictors, etc.) for improving water usage.
Implementation strategies
Following thorough data collection and economic analysis, ISTC can construct implementation strategies for efficiency projects that have been ranked as the highest priority. Strategies seek to maximize impact while minimizing disruption.

WatcH20 can provide comprehensive wastewater evaluation and process recommendations to wastewater treatment plants. Benefits to POTWs include:
- Reduced influent contaminants and loads
- Reduced BOD, TSS, FOG, heavy metals, and slug loads
- Improved wastewater treatment efficiencies
- Increased plant capacity
- Increased energy efficiency and energy savings
Recent Success–Health Service
Type of Assistance: Water Use Assessment and Recommendations
Highlights:
- Collected usage data and created process map
- Created water balance to match uses with supply
- Calculated the full cost of processed water
- Analyzed water efficiency opportunities for equipment upgrades
- Provided full report with priorities identified including costs, payback periods, and water usage reduction.
For more successes and case studies, visit the ISTC web site. To schedule a free site visit from TAP engineers, go to www.istc.illinois.edu/sitevisit.


 The Construction Engineering Research Laboratory (CERL), a division of the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers’ Engineer Research and Development Center (ERDC), has paired with ISTC on several research projects over the years but it wasn’t until about two years ago with the arrival of ISTC’s current director, Kevin O’Brien that the relationship deepened.
The Construction Engineering Research Laboratory (CERL), a division of the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers’ Engineer Research and Development Center (ERDC), has paired with ISTC on several research projects over the years but it wasn’t until about two years ago with the arrival of ISTC’s current director, Kevin O’Brien that the relationship deepened.









 The technology demonstration was one of ISTC’s Billion Gallon Water Challenge (BGWC) research projects which aimed at saving freshwater resources at multiple levels. A case study on this and other
The technology demonstration was one of ISTC’s Billion Gallon Water Challenge (BGWC) research projects which aimed at saving freshwater resources at multiple levels. A case study on this and other