ISTC’s Billion Gallon Water Challenge has released a video of its research collaboration with American Water and Echologics to demonstrate new leak detection technology for residential drinking water distribution systems.
Last year the research partners tested the effectiveness of Echologics’ acoustic sensors (designed to be permanently) placed in fire hydrants in a greater Chicago neighborhood — in a multi-channel wireless network to provide real-time 24/7 leak detection in buried distribution systems and demonstrated accuracy of 90 percent.
 The technology demonstration was one of ISTC’s Billion Gallon Water Challenge (BGWC) research projects which aimed at saving freshwater resources at multiple levels. A case study on this and other BGWC research is available on ISTC’s website. The technology demonstration was also featured by EfficientGov.com in “Sound Sensors Can Detect Water Pipe Leaks.”
The technology demonstration was one of ISTC’s Billion Gallon Water Challenge (BGWC) research projects which aimed at saving freshwater resources at multiple levels. A case study on this and other BGWC research is available on ISTC’s website. The technology demonstration was also featured by EfficientGov.com in “Sound Sensors Can Detect Water Pipe Leaks.”
In the BGWC video, Kevin Hillen, Illinois American Water operations superintendent, explains that 12-15 percent of water in the Chicago area is lost to leaks. As water pipe infrastructure continues to age, a greater proportion of potable water will be lost without proactive leak detection and pipe replacement efforts, he added.
“Leaks have a distinct sound signature,” according to Eric Stacey, Echologics product manager. “Leaks occur in specific frequency bands for different materials of pipe,” he explained. In cast iron pipes, for instance, leaks produce a sound at about 300 Hz. “It’s audible, the human ear can hear it, and it stands out from a normal pipeline operation.”
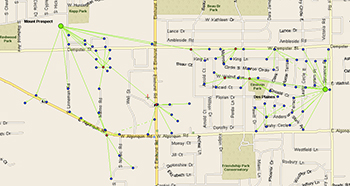
Economics determines the acceptable level of leakage in a water system. In suburban Chicago, where the cost of water exceeds $5 per 1,000 gallons, the necessity of minimizing leaks is greater than average. At the lower end, water can be delivered in some areas for as little as $0.35 per 1,000 gallons.
The installation successfully zeroed in on leaks forming in the American Water distribution system in a neighborhood near Des Plaines, IL. Correlating the data with specialized algorithms, “we were able to show leaks that formed and we were able to show water savings,” Stacey said.
BGWC research is funded by the Illinois Hazardous Waste Research Fund.

