September is a time to think about pollution prevention, aka P2, because the third week of September every year is celebrated as Pollution Prevention (P2) Week in the U.S. In 2023, P2 Week will be September 18-22. As you mark your calendar, you may ask yourself—what exactly is pollution prevention, and how can I contribute to the effort?
First, let’s take a moment to consider what pollution itself is. The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) defines pollution as “any substances in water, soil, or air that degrade the natural quality of the environment, offend the senses of sight, taste, or smell, or cause a health hazard. The usefulness of the natural resource is usually impaired by the presence of pollutants and contaminants.” So, pollution is the contamination of the environment by potentially harmful substances. If you think of a polluted environment as analogous to a human body with harmful chemicals in it or disease, then it’s easy to think of pollution prevention as analogous to disease prevention. You’ve probably heard the old quote from Benjamin Franklin, “An ounce of prevention is worth a pound of cure.” Although Franklin was talking about the prevention of house fires, in modern times, the phrase has come to be used in the sense of health care. It means that taking preventative measures (e.g., exercising, watching what you eat, getting enough sleep, etc.) is a much more sensible strategy to take, wherever possible, than waiting until disease sets in and then working to treat it. It’s far better to avoid a problem than to have to try to solve the problem afterward.
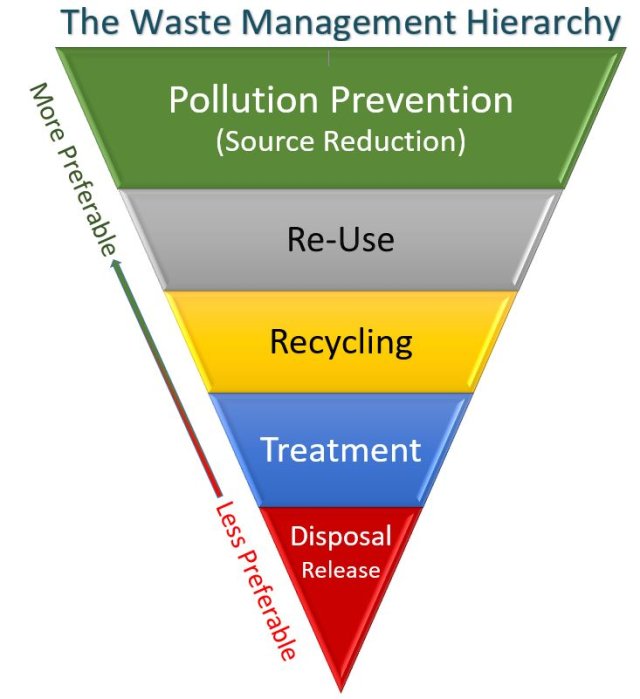
Thus, pollution prevention is the sensible strategy of preventing the release of harmful substances into the environment, aka source reduction, to avoid the negative impacts of pollution and the cost, time, energy, and other resources that would otherwise need to be expended on environmental clean-up after the fact. Or, as the U.S. EPA states, pollution prevention is “actively identifying equipment, processes, and activities which generate excessive wastes or use toxic chemicals and then making substitutions, alterations, or product improvements.” P2, or source reduction, “is fundamentally different and, where feasible, more desirable than recycling, treatment or disposal. It is often more cost effective to prevent pollution from being created at its source than to pay for control, treatment and disposal of waste products. When less pollution is created, there are fewer impacts to human health and the environment.”
P2 practices for manufacturing and industrial sectors might entail using less toxic cleaners, less hazardous ingredients or process inputs, conserving energy and water, and reducing waste through the reuse of materials such as drums or pallets. Manufacturers and supporting industries in Illinois can also contact the Illinois Sustainable Technology Center (ISTC ) Technical Assistance Program (TAP) to learn more about U.S. EPA-funded P2 assistance available free of charge to members of the aerospace, automotive, chemical, food and beverage, and metal manufacturing and fabrication sectors. See https://uofi.box.com/s/ypoep56408o4kk5pl0qpt2ojpwyo82qh and https://uofi.box.com/s/1crril27e0td9nd3j3njgh49mzoom0q5 for details.
The principles of P2 can be applied to any sector or effort and in homes and schools. It’s all about more efficient use of valuable resources, such as energy and water, using less-toxic materials and products, and avoiding the generation of waste so you don’t have to deal with as many disposal considerations. So, if you practice waste reduction by eliminating disposable products and single-use plastics, if you purchase and use energy-efficient appliances and weatherize your home for the winter, if you look for and fix leaky pipes or faucets, or if you use safer cleaners, you’re practicing P2!
Use the following resources to learn more about P2 and how you can contribute to “preventative medicine” for environmental health and our collective human health which depends upon a healthy environment.
- U.S. EPA–Learn About Pollution Prevention
- U.S. EPA—Pollution Prevention Law and Policies (For example, have you heard of the Pollution Prevention Act of 1990?)
- U.S. EPA—Pollution Prevention Week
- U.S. EPA—Pollution Prevention Tips at Home
- National Pollution Prevention Roundtable (NPPR)
- U.S. EPA—Safer Choice
- U.S. EPA—Institutional Purchasers of Green Products and Services
- U.S. EPA—Green Chemistry
- Green Science Policy Institute–Six Classes (reducing exposure to chemicals of concern)
- U.S. EPA—Green Building Standards
- ENERGY STAR
- U.S. EPA–WaterSense
- ISTC Technical Assistance Program—Schedule Your Free Site Visit










