Mark your calendars for Food Waste Prevention Week, scheduled to take place April 1-7 this year.
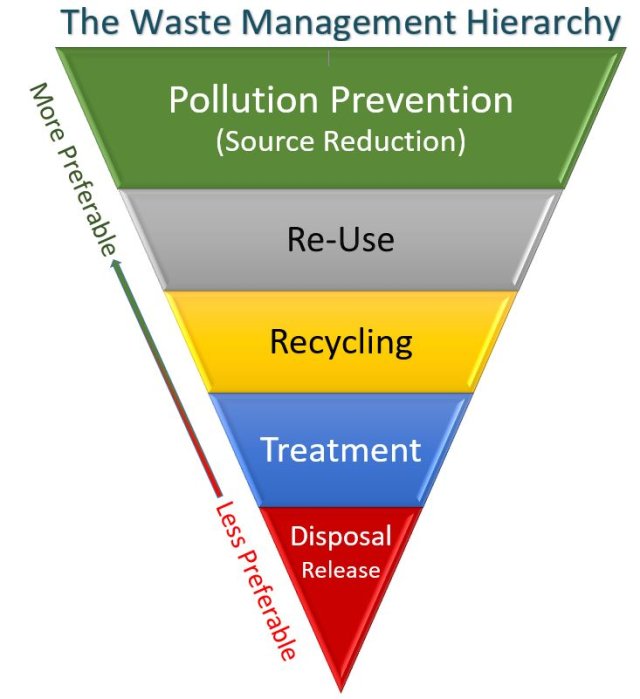
In 2019 alone, EPA estimates that about 66 million tons of wasted food were generated in the food retail, food service, and residential sectors, and most of this waste (about 60%) was sent to landfills. Food Waste Prevention Week is a collaborative effort to raise awareness about food waste and its negative impacts on our society and environment, while also sharing resources to help individuals, families, and organizations reduce their own food waste. Because its Technical Assistance Program (TAP) has experience working on food waste reduction and management projects, the Illinois Sustainable Technology Center is proud to be a partner organization for Food Waste Prevention Week for the second year in a row!
Be sure to check ISTC’s social media platforms during April 1-7, as we highlight some of the past and present work TAP is doing related to food waste, as well as facts and resources to help you on your food waste reduction journey. If you’re not already following us on social media, you can connect with us on:
- Facebook at https://www.facebook.com/ISTCatUIUC,
- X at https://twitter.com/ISTCatUIUC, and on
- LinkedIn at https://www.linkedin.com/company/illinois-sustainable-technology-center/.
Throughout the week, several partners across the U.S. will host webinars to inspire action to reduce food waste. For example:
- Closing the Loop. On Monday, April 1, at noon Central, join an informative discussion on what food waste generators can do to sustainably process their waste via on- and off-site composting, biodigesters, anaerobic digesters, etc. Register here.
- Harnessing the Power of Food Preferences for Overproduction Reduction. Unveil how individual eating preferences can be a game-changer in minimizing food waste in food services. Learn how culinary IDs are the key to precise production while offering diners a better, personalized experience at scale. This webinar will be on April 1 from 1-1:50 PM Central time. Register here.
- USDA Programs, Investments, and Innovations to Prevent and Reduce Food Loss and Waste. On April 2, from 11 AM to noon Central, join Dr. Jean Buzby (USDA Food Loss and Waste Liaison) and a panel of leaders from across USDA (NIFA, OUAIP, FNS, and ARS) to learn about some of the ways the agency engages in food loss and waste prevention and reduction across the U.S. food supply chain. Register here.
- Gleaning: Reduce Loss & Waste at the Farm. On April 3 from 3-3:50 PM Central, join the Society of St. Andrew’s experts on gleaning and learn about its impact. They will discuss the benefits of gleaning crops for farmers, local hunger relief agencies, and volunteers alike, the impact of SoSA’s work over 40+ years, and ways to get involved in your locale. Register here.
- Food Production and Sustainability. This thought-provoking panel discussion of industry experts will explore the industrial perspective of the fight against food waste and share strategies for implementing sustainability without compromising operational effectiveness. Join the discussion April 4th from 10-10:50 AM CDT. Register here.
- From Food Scraps to Soil Food: Starting a Drop-Off Program in Your Community. Learn how East Hampton Compost is growing awareness of food waste, diverting scraps from the waste stream and enriching local soils. A collaboration between ReWild Long Island and the Town of East Hampton, with local high school students staffing drop-off locations and working on outreach. Dive into the dirt to gain valuable insights into the challenges and rewards of piloting an all-volunteer initiative, as well as actionable strategies for starting one in your community. This webinar will be on April 4 from 2-2:50 PM. Register here.
See the Food Waste Prevention Week “Webinars” page for additional webinars scheduled for Food Waste Prevention Week, and learn more about other ways you can get involved at https://www.foodwastepreventionweek.com/get-involved.