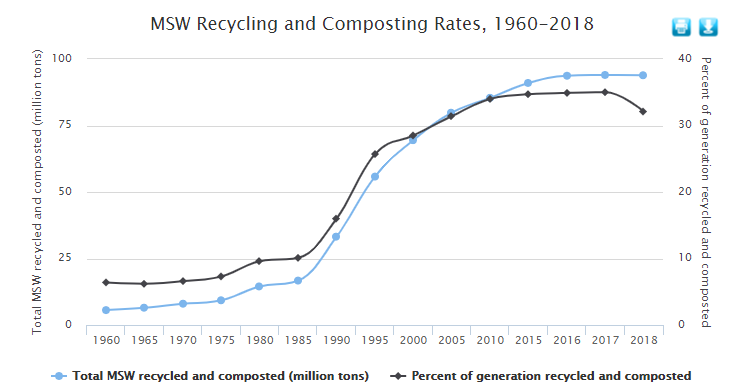
On November 17, 2022 the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) announced the availability of $100 million in grants for recycling infrastructure and recycling education and outreach projects throughout the country.
The Solid Waste Infrastructure for Recycling (SWIFR) Grant Program is divided into several funding opportunities. Information on the State and Territory Grant Program and the Political Subdivisions Grant Program is currently available on the U. S. EPA website, with information on the Tribal Grant Program coming soon.
SWIFR Political Subdivisions Grant Program
Entities eligible to apply for funding through the SWIFR Political Subdivisions Grant Program include “Political subdivisions” of states and territories, such as counties, cities, towns, parishes, and similar units of governments that have executive and legislative functions to be political subdivisions of states and territories.
Applications Due: January 16, 2023
Notice of Intent to Apply Deadline: December 15, 2022
Funding Available: The minimum individual award amount is $500,000 and the maximum individual award is $4,000,000 for the grant period.
Grant Period: Up to 3 years
Materials and waste streams considered under this announcement include:
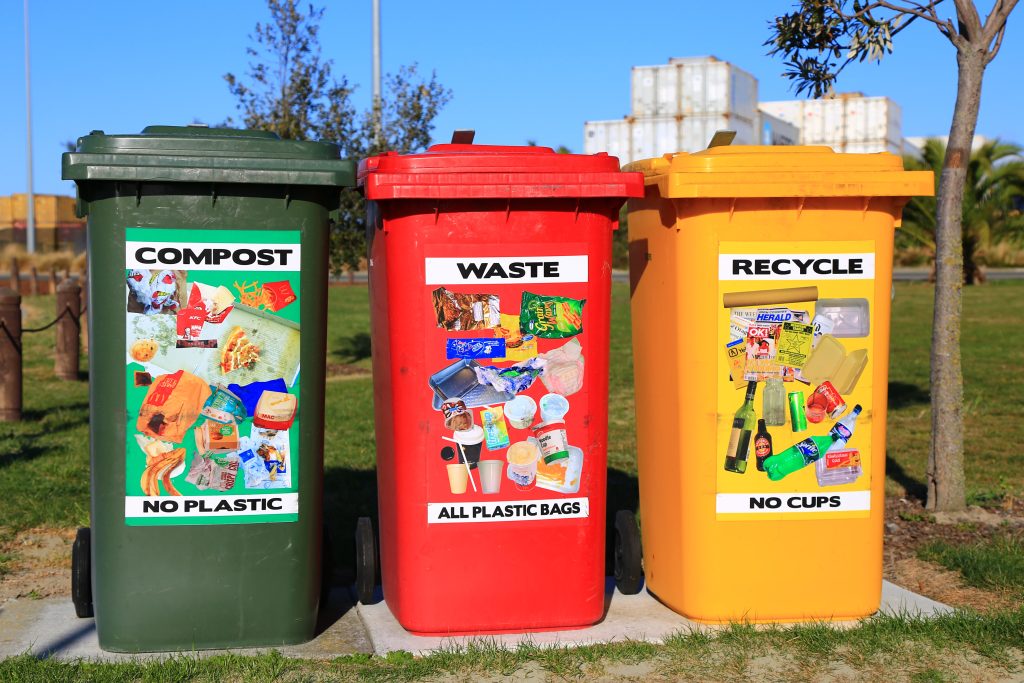
- Municipal solid waste (MSW), including plastics, organics, paper, metal, glass, etc. and construction and demolition (C&D) debris.
- In addition, materials and waste streams considered include the management pathways of source reduction, reuse, sending materials to material recovery facilities, composting, industrial uses (e.g., rendering, anaerobic digestion (AD)), and feeding animals.
All applications must achieve one or more of the following objectives:
- Establish, increase, expand, or optimize collection and improve materials management infrastructure.
- Fund the creation and construction of tangible infrastructure, technology, or other improvements to reduce contamination in the recycled materials stream.
- Establish, increase, expand, or optimize capacity for materials management.
- Establish, improve, expand, or optimize end-markets for the use of recycled commodities.
- Demonstrate a significant and measurable increase in the diversion, recycling rate, and quality of materials collected for municipal solid waste.
Eligible activities include (but are not limited to):
- Innovative solutions and/or programs that provide or increase access to prevention, reuse, and recycling in areas that currently do not have access; including development of and/or upgrades to drop-off and transfer stations (including but not limited to a hub-and-spoke model in rural communities), etc.
- The purchase of recycling equipment, including but not limited to sorting equipment, waste metering, trucks, processing facilities, etc.
- Upgrades to material recovery facilities (MRFs) such as optical sorters, artificial intelligence, etc.
- Development of and/or upgrades to composting facilities or anaerobic digesters to increase capacity for organics recycling.
- Development of and/or upgrades to curbside collection programs or drop-off stations for organics.
- Development of and/or upgrades to reuse infrastructure such as online reuse platforms, community repair spaces, technology and equipment to improve materials management reuse options, food donation, and upcycling, staging areas for material reuse/donation, reuse warehouses, and reuse centers, and electronic waste and computer recycling and refurbishing.
Recycling Education and Outreach (REO) Grant Program
The REO Grant Program includes $30 million in funding for projects to improve consumer education and outreach on waste prevention, reuse, recycling, and composting. The grants aim to reduce waste generation, decrease contamination in the recycling stream, and increase recycling rates across the country in a manner that is equitable for all.
Eligible applicants include:
- U.S. States, including Washington, D.C.
- Puerto Rico, Virgin Islands, Guam, American Samoa, Commonwealth of Northern Mariana Islands.
- Local governments.
- Federally recognized tribal governments.
- Native Hawaiian organizations, Department of Hawaiian Home Lands, Office of Hawaiian Affairs.
- Nonprofit organizations.
- Public-private partnerships.
Applications Due: January 16, 2023
Notice of Intent to Apply Deadline: December 15, 2022
Funding Available: The minimum individual award floor is $250,000, and the maximum individual award ceiling is $2,000,000 for the grant period.
Grant Period: Up to 3 years
Materials within the scope of this grant program include commonly recycled materials, such as aluminum and steel containers, glass, cardboard paper, and plastics, as well as food, organics (yard and tree trimmings, wood, etc.), textiles, batteries, and electronics. Also within the scope of this grant program are education and outreach activities that prevent or reduce waste by reducing, reusing, repairing, refurbishing, remanufacturing, recycling, composting, or using anaerobic digestor systems to treat these types of materials or to reduce related contamination.
All projects must encourage the collection of recyclable materials and must achieve one or more of the following objectives:
- Inform the public about residential or community recycling programs.
- Provide information about the recycled materials that are accepted as part of a residential or community recycling program that provides for the separate collection of residential solid waste from recycled material.
- Increase collection rates and decrease contamination in residential and community recycling programs.
Eligible activities include (but are not limited to):
- Public service announcements.
- Door-to-door education and outreach campaigns.
- Social media and digital outreach.
- An advertising campaign on recycling awareness.
- The development and dissemination of:
- a toolkit for a municipal and commercial recycling program.
- information on the importance of quality in the recycling stream.
- information on the benefits of recycling.
- information on what happens to materials after the materials are placed in the bin.
- Businesses recycling outreach.
- Bin, cart, and other receptacle labeling and signs.
- Community ambassador education programs or training the trainer programs.
- Other education and outreach activities to improve waste prevention, reuse, and recycling, and reduce contamination, such as evaluations and evidence-based messaging and strategies associated with preventing or reducing waste and improving reuse, repair, refurbish, and remanufacture of materials.
Learn more