 The University of Illinois at Chicago (UIC) recently released a Sustainable Materials Management Plan, a concrete step in the university’s goal to become a Zero Waste Campus.
The University of Illinois at Chicago (UIC) recently released a Sustainable Materials Management Plan, a concrete step in the university’s goal to become a Zero Waste Campus.
During the past academic year, many stakeholders observed current waste management practices and coordinated and conducted a waste characterization study to represent campus-wide activities. Study results and annual material generation data were analyzed and extrapolated, campus focus groups were held to provide input for ideal material management, and the research and recommendations were collated into one comprehensive plan to increase waste diversion and ultimately achieve a zero-waste campus.
UIC partnered with the Illinois Sustainable Technology Center’s (ISTC) Technical Assistance Program to conduct the waste audit, engage stakeholders, and spearhead plan development. The plan identifies nearly 100 strategies for waste reduction and diversion and was informed by the results of a November 2019 waste audit, along with insightful input received from students, faculty, staff, and community members.
UIC’s Waste Characterization Study
The waste characterization study included more than 3,300 pounds of trash from 14 buildings and outdoor campus collection bins sorted into 32  material categories.
material categories.
The audit team used an activity zone approach to capture waste from buildings by use, such as administrative offices, academic and lab settings, student residence halls, and multi-use spaces.
Landfill and recycling bins from various outdoor areas of campus, such as along internal walking paths, busy urban corridors, and in parking structures, comprised an “On-the-go” activity zone. The study team and an enthusiastic group of student, staff, and faculty volunteers sorted the waste over the course of a wintery week.
UIC’s Sustainable Materials Management Plan
Co-led by ISTC, and UIC’s Office of Planning Sustainability and Project Management (PSPM), a team of staff, faculty, and students from various departments, external partners and industry experts developed the Sustainable Materials Management Plan.
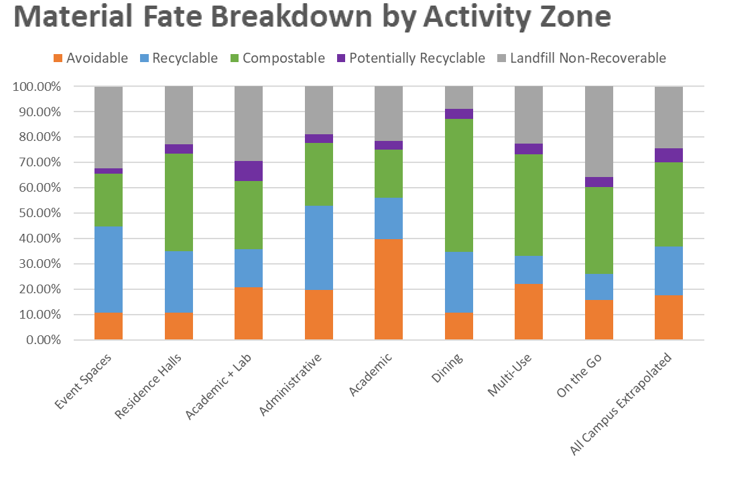
Together team members worked to document and understand current waste management practices and analyzed waste generation. The Plan categorizes campus waste to show what is avoidable, currently recyclable, compostable, potentially recyclable, and non-recoverable.
The data revealed that 33% of the overall waste stream on campus is compostable material, such as food scraps. Nineteen percent of the waste stream is composed of recyclable materials such as paper or plastic bottles. Eighteen percent of the waste stream on campus consists of avoidable materials such as paper towels and disposable beverage cups. Five percent of the waste stream is comprised of potentially recyclable material such as plastic film and gloves that could be diverted through source-separated streams.
The remaining 24% of the waste stream consists of materials that are currently non-recoverable, i.e. items for which recovery end markets or programs do not yet exist, or for which solutions are not yet available at UIC or in surrounding areas. This includes items like single-use equipment and other non-recyclable paper, glass and plastic items.
“Data has been a critical part of our success in reaching almost a 50% recycling rate at UIC over the past decade, even while the number of students on campus has grown by 20%. With the help of data, the recycling program at UIC has vanquished a once prevalent view that Chicago doesn’t recycle. With the report from the ISTC led waste audit, the volume of food scraps, and the presence of currently recyclable materials point to impactful steps we must take in waste reduction, outreach, and education,” stated Joe Iosbaker, UIC’s Recycling Coordinator.
The study team also gathered input from members of the campus community through an online survey and a series of focus groups. Discussions shed light on knowledge, perceptions, and expectations of waste management infrastructure, the overall campus culture surrounding resource recovery, waste-related priorities, and challenges. This feedback from the UIC community was used to develop strategies to increase recycling and waste reduction. Through this multi-layer process, UIC now has a comprehensive roadmap to build from the 47% recycling rate today and prime the conditions for a zero-waste campus by 2050.
“The comprehensive presentation in the Materials Management Plan provided by ISTC gives us a greater understanding of the tasks we have,” Iosbaker asserted. Assistant Vice-Chancellor and Director of Sustainability Cindy Klein-Banai reinforced those sentiments stating, “This study has provided the data and next steps for robust strategies for reaching our Zero Waste Goal within the UIC Climate Commitments. It also demonstrates the need for broad responsibility in developing our program across all units and departments of the university.”
“ISTC’s Zero Waste team acknowledges the great potential of a comprehensive, campus-driven Sustainable Materials Management Plan,” shared April Janssen Mahajan, Sustainability Specialist at ISTC. “We fully embraced the challenges and opportunities this project offered to help UIC reconsider, reimagine and redefine campus waste and materials management in support of the university’s mission to become a Zero Waste Campus.”





 The
The  material categories.
material categories. 
 With the start of a new year, ISTC’s Institutional Water Treatment (IWT) program is offering a new service to test water sources for Legionella, the bacterium that causes Legionnaires’ disease, to decrease exposure for clients with weak immune systems.
With the start of a new year, ISTC’s Institutional Water Treatment (IWT) program is offering a new service to test water sources for Legionella, the bacterium that causes Legionnaires’ disease, to decrease exposure for clients with weak immune systems.